OSI Model Explained
OSI refers to Open System interconnection. It is a framework that acts as a reference to Networking and is first developed around 1984 in the name of ISO. It offers a top-level overview of transferring information from one HostHost to another host. The term "network" can be described as a group of interconnected computers—typically known as the HostHost, which communicates with one another via earphones to exchange data. Networking is creating a network based on protocols and hardware, software media, etc. and the data transfer between the devices on the web.
Related posts
OSI Model
OSI Model follows the model of the Layered System. OSI Model is based on the architecture known as Philosopher translator Secratory architecture.
What is the OSI model?, Source: Youtube, RealPars
In this structure, it is a case of two intelligent beings (A and B) located in different places, and they don't have the same languages and want to send information. Therefore, specific steps must follow by each to successfully transmit the message.
Specifications of the OSI Model
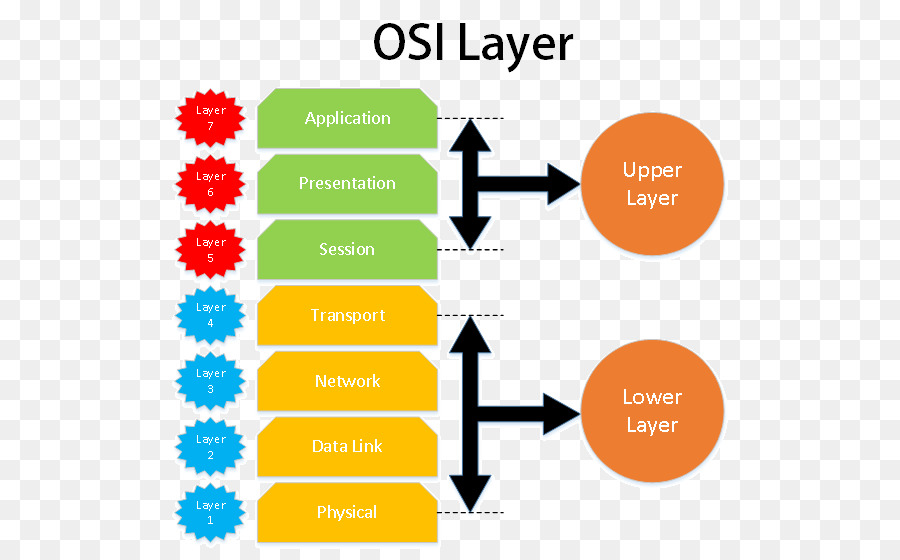
OSI model is split into two distinct groups. One group is responsible for the HostHost, while the other is for the Network.
The layers that fall in the responsibilities of the Host include:
- Application Layer
- Present Layer
- Session layer
- Transport Layer
The layers that fall within the responsibility of the Network are :
- Network Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Physical Layer
Hosts' responsibility is the following: encryption, session management, Segmentation, Flow Control, and more.
The obligations of the Network such as - route to router packet congestion management, network identification, etc.
OSI Model Layers
OSI Model has seven different layers, which we have covered in the details of the OSI Model. Let's now look at a detailed perspective of these layers.
Application Layer
This Layer handles the application component. Applications that require connectivity to the Network and the protocols defined in the Layer for application are followed by applications to transmit data.
The Application layer is a collection of protocols. The protocols look as follows:
CCNA1-ITNv7 - Module 15 - Application Layer, Source: Youtube, Arthur Salmon
Browser HTTP/HTTPS FTP
Outlook --"SMTP
Skype-- Skype Protocol
Remote Desktop --- Telnet, RDP.
This is the entire application that operates on the client-side. It also has a set of protocols the application uses based on its communication capabilities.
HTTPS HTTPS It is the version that is secure of HTTP. It states that it securely transmits the information via the internet—Ex - password, card details, etc.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is utilized to transfer files between a computer and another.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) can transfer and send an email on the internet.
Present Layer
It is accountable for three main tasks.
- Transformation –It converts the information received by the Layer of application to the format that is ASCII (American Standard Code for Interchange) Codes and UNICODE to Binary Format.
Example -Data Hello. Thus, the ASCII Code associated with it is 72 101 108, 108, 111. The next Binary Code is - 01001000 01100101 01101100.
So, this is the very first thing the presentation layer will perform following the receipt of the information received from the Layer of application.
Lec-74: Presentation layer in computer networks in Hindi | OSI Model, Source: Youtube, Gate Smashers
ExampleSuppose there is an image with a size of 1MB. Data Compression attempts to reduce these dimensions to be less than 1MB.
Also, this is done through the Presentation Layer to facilitate communication.
- Encryption's purpose is to decrypt the data so that it isn't recognized by hackers who could see the data and use it to commit fraud. Similar to HTTPSuses SSL (Secure Socket Layer) protocols to secure the data.
For example, suppose you want to share the password or any other confidential information, then sending a plain text message might make it unsecure. This is why the presentation layer secures the Data by encrypting it and transmits it via the Network.
Example In the image above, we can see that compression decreases its size. Also, the message (Plain Text) is encrypted into encrypted Text (Cipher Text). This is all handled in the present Layer.
Session Layer
Session Layer handles the session control for the connection to the internet. It performs a variety of things.
Establish Connections, Manage and Terminate them (HTML0) –Establishment of Connection refers to establishing an internet connection where both client and server have consented to share information.
Lec-73: Session Layer of OSI model | Session layer functions in Hindi, Source: Youtube, Gate Smashers
Description -In the above examples, the person is trying to enter the office, and security personnel asks the individual to sign in. The person will then provide the user Id and password to verify. This is known as authentication. To confirm if the individual is authentic or not.
The same method is used in the Layer for a session in the OSI Model, which also assists in authenticating and checking the authorization process to allow access.
Transport Layer
It is responsible for what is known as"
Segmentation: Segments are small segments of data separated from the bulk of data. If we're given 10 M.B. of data, then the entire 10 M.B. data is broken down into parts, each of which is 1 M.B. in size.
Flow Control: Flow control controls the flow of information that is transferred from hosts to one another.
The Sender may be transmitting data Reciever at 10MBPS Transfer Rate. However, Reciever cannot process the data at 10MBPS. It only processes data at 1MB/s.
OSI Model (Part 2) - Transport layer and Network Layer , Source: Youtube, TechTerms
The receiver then asks the server for a 1MBPS rate of transfer since it cannot deal with the info. Then the Sender will send the data at a 1MBPS rate.
This is also known as Flow Control.
- Error control manages the errors in data. If there's an error with the data, it assists in resolving the data.
- Let's say Sender sends information using four segments if the third segment is missing in the middle. Error control can help repair the issue.
- It is a part of a system that can aid in fixing this Data. For instance, Automatic Repeat Request. The segment that doesn't have a receiver is sent to the recipient. It will then ask you to send it again.
In addition to these essential aspects, Apart from these general things, the Transport layer also integrates data contained in the packet received by the network layer. It does this based on its sequence numbers.
Network Layer
After encapsulating it with the destination and source I.P. Address, it is the one that generates the packet. The general format of the box is like this:
- What exactly is I.P. Address? It is the Address. It is identified. It is a 32-bit or 4-byte Address (in IPv4), and each bit has an address space of 0-255. It is known as an Octet.
- The Layer's job that is network-related is to assign an I.P. address to each HostHost. Also, it performs something known as routing.
OSI Model: The Network Layer, Source: Youtube, Chris H.
What's Routing? Routing refers to setting the packet's route that will take it from the Sender's end to the receiver.
- What does a router do to accomplish this? The router does this when it receives the I.P. address of its destination and then performs something known as masking.
- Masking is an easy bitwise operation. The router sets a few bits to 0 and executes a procedure that is bitwise AND which, after masking the I.P. address that is intended for the destination, will receive the Network's I.P. address.
Then, with the help of the I.P. address of the Network, it will determine the next router to use for the Data it will transmit.
Path Determination: What does it mean? What? There could be several ways I could send a packet to its destination. The goal in Path Determination is to find the most efficient route to transmit the package quickly and in less time.
Data-Link layer packet is transmitted via the network layer. On that packet, the headers are included along with the Source and Destination MAC address.
- The MAC address (Media Access Control) is 48-bit, or 6-byte long, comprising a Hexadecimal code. This is the number that is explicitly assigned to every network device.
- It is also known as physical Address since it is the physical Address of the network device through where Data is transferred.
- This is assigned to network devices, such as NIC(Network Interface Card), WiFi Card USB WiFi Dongle, and others. from the company that makes it.
Error detection is the way to identify any errors in the data. This is a way of determining if the data was received correctly or not.
Specific algorithms can help check that. Like - CRC (Cyclic redundancy check), Checksum, Bit Parity, etc.
These three actions mentioned earlier are fundamental to the Data Link layer. It takes in data as a stream of bits, and it receives the data from the Physical Layer. It looks for headers and then identifies the MAC address, which is a valid one and belongs to a paired device, or not.
Physical Layer
Data Link, Layer Data Link layer, gives a frame. The frame must be sent towards the desired destination. The Data is composed of bits. Physical Layer converts data into the appropriate signal and sends it to the Network.
Physical layer in OSI Model | Physical layer Protocols | Physical Layer Tutorial | networking tip, Source: Youtube, ISO Training Institute
Physical Layer also handles the process of encoding bits in the signals. The appropriate signal can be described as the data in the shape of an electrical pulse, laser beam, etc.
Explanation In the image above, Data is encoded to the manchester encoder following the clock pulse.
Conclusion
OSI Model is the basic model that functions as the reference model for implementing the Network or for designing the Network for reality.
The model is being implemented daily as the TCP/IP, with the layers described within the OSI model. OSI model. Various algorithms aid in transferring data from the hosting server to the final destination.
Related posts
Make the most of the features of your Android phone by altering these settings
Why do programmers get so rude? 3 main reasons
Thanks for reading.
Source: https://proreviewsapp.com/







Leave a Reply
Your e-mail address will not be published. Required fields are marked *